Graphite is an allotropic isomer of carbon, a gray-black, opaque solid, chemically stable, corrosion-resistant, and not easily reacted with acids, alkalis and other agents. Natural graphite comes from graphite deposits, or petroleum coke, asphalt coke and other raw materials, after a series of processes to make artificial graphite. Graphite burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, and can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents such as concentrated nitric acid and potassium permanganate. It can be used as anti-wear agent, lubricant, high purity graphite is used as neutron reducer in atomic reactor, and also can be used to manufacture crucible, electrode, brush, dry cell, graphite fiber, heat exchanger, cooler, electric arc furnace, arc lamp, and pencil lead.
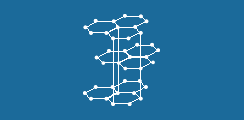
Graphite is a transition crystal between atomic, metallic and molecular crystals. In the crystal between the same layer of carbon atoms to sp2 hybridization to form covalent bonds, each carbon atom and the other three carbon atoms associated with six carbon atoms in the same plane to form a positive hexagonal ring, stretching to form a lamellar structure. In the same plane of the carbon atoms are also left each a p orbital, they overlap each other, forming off-domain π bond electrons in the lattice can move freely, can be excited, so graphite has a metallic luster, can conduct electricity, heat transfer. As the distance between the layers is large, the bonding force (van der Waals force) is small, the layers can slide, so the density of graphite is smaller than diamond, soft and slippery.
The distance between each net layer of graphite is 3.40Å, which is bonded by van der Waals forces, i.e., the layers belong to molecular crystals, and the spacing of the carbon atoms in the same net layer is 1.42Å. Since the bond between carbon atoms on the same planar layer is very strong and extremely difficult to be broken, the melting point of graphite is also very high and its chemical properties are stable. In view of its special bonding method, it cannot be singularly considered as a single crystal or polycrystal, and it is now generally recognized that graphite is a mixed crystal.
Graphite is soft, black gray, hardness is 1 ~ 2, along the vertical direction with the increase of impurities and its hardness can be increased to 3 ~ 5. Specific gravity is 1.9 ~ 2.3. specific surface area range is concentrated in the 1-20m2 / g, in the isolation of the oxygen conditions, the melting point of more than 3000 ℃, is one of the most temperature-resistant minerals. It can conduct electricity and heat.
There is no such thing as pure graphite in nature, which often contains impurities such as SiO2, Al2O3, FeO, CaO, P2O5, CuO and others. These impurities often appear in the form of minerals such as quartz, pyrite, carbonate and so on. In addition, there are water, asphalt, CO2, H2, CH4, N2 and other gas parts. Therefore the analysis of graphite, in addition to the determination of fixed carbon content, but also must be measured at the same time the content of volatile matter and ash.
The electrical conductivity of graphite is one hundred times higher than that of ordinary non-metallic minerals. Thermal conductivity exceeds steel, iron, lead and other metal materials. The coefficient of thermal conductivity decreases with increasing temperature, and even at very high temperatures, graphite becomes an adiabatic body.
The lubricating properties of graphite depend on the size of the graphite scales; the larger the scales, the smaller the coefficient of friction and the better the lubricating properties
Graphite has good chemical stability at room temperature and is resistant to acids, alkalis and organic solvents.
When used at normal temperatures, graphite can withstand drastic changes in temperature without damage, and when the temperature changes suddenly, the volume of graphite does not change much and cracks do not appear.
Graphite can be divided into two categories, natural graphite and artificial graphite, natural graphite from graphite deposits, natural graphite can also be divided into scaled graphite, earthy graphite and lump graphite. The main use of natural graphite is the production of refractory materials, brushes, flexible graphite products, lubricants, lithium-ion battery anode materials, etc., the production of some carbon products sometimes also add a certain amount of natural graphite.
The largest production in the carbon industry is a variety of artificial graphite products, artificial graphite products are generally easy to graphitization of petroleum coke, asphalt coke as raw materials, through the ingredients, mixing and kneading, molding, roasting, graphitization (high-temperature heat treatment) and a series of mechanical processing and other processes and made.
There are also many types of artificial graphite, such as single crystal graphite, polycrystalline graphite, pyrolytic graphite, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, polyimide synthetic graphite, graphite fibers and so on. Most artificial graphite products belong to polycrystalline graphite. The main products of artificial graphite are graphite electrodes used in electric arc steelmaking furnaces and mineral heat furnaces, graphite electrodes are a kind of conductive material that is resistant to high temperature and corrosion. Artificial graphite in many other industrial sectors also has a wide range of uses, such as the mechanical industry, motor brushes, precision casting molds, EDM molds and wear parts, the chemical industry used in the electrolysis tank or corrosion-resistant conductive equipment, the nuclear industry sector of high purity and high strength artificial graphite is the structure of the reactor materials and used as components of missiles and rockets and so on.
Graphite deep processing industry is the premise of purification, graphite purification is a complex physical and chemical process, its purification methods are mainly flotation method, alkaline acid method, hydrofluoric acid method, chlorination roasting method, high temperature method.
Flotation is a commonly used and important beneficiation method, graphite has good natural floatability, basically all graphite can be purified by flotation, in order to protect the graphite scales, graphite flotation mostly adopts multi-stage process. Graphite flotation capture agent is generally used kerosene, the dosage is 100-200g/t, the foaming agent is generally used turpentine oil or butyl ether oil, the dosage is 50-250g/t.
The alkaline-acid method consists of two reaction processes: the alkali fusion process and the acid leaching process. Alkali fusion process is in high temperature conditions, the use of molten alkali and graphite in the acidic impurities in the chemical reaction, especially the impurities containing silicon (such as silicates, silicon-aluminate, quartz, etc.), the generation of soluble salts, and then washed to remove impurities, so that graphite purity can be improved. The basic principle of the acid leaching process is to use acid and metal oxide impurities reaction, this part of the impurities in the alkali fusion process did not react with alkali. So that the metal oxides into soluble salts, and then washed to make it separate from graphite, after the combination of alkali fusion and acid leaching of graphite purification has a better effect.
Hydrofluoric acid is a strong acid that can react with almost any impurities in graphite, and graphite has good acid resistance, especially to hydrofluoric acid, which determines that graphite can be purified with hydrofluoric acid. The main process of hydrofluoric acid method is that graphite and hydrofluoric acid are mixed, hydrofluoric acid and impurities react for a period of time to produce soluble substances or volatiles, the impurities are removed by washing, and the purified graphite is obtained by dehydration and drying.
Chlorination roasting method is the graphite and certain reductant mixed together, in a specific equipment and atmosphere under high temperature roasting, material valence metal into gas phase or condensed phase metal chloride, so that the graphite purification process.
Graphite impurities in high temperature conditions, can be decomposed into higher melting point oxides, such as SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, CaO, MgO. these oxides in a certain high temperature and the atmosphere, pass into the chlorine, metal oxides and chlorine reaction to generate lower melting point of chloride. So at a lower temperature, these chlorides can be vaporized and escape, to achieve separation from graphite, so that graphite can be purified
The melting point of graphite is 3850℃±50℃, which is one of the substances with the highest melting and boiling point in nature, much higher than the boiling point of impurity silicate. Using the difference of their melting and boiling points, graphite is placed in graphitized graphite crucible and heated up to 2700℃ by using specific instruments and equipment, which can make the impurities gasify and escape from the graphite to achieve the effect of purification.
High-temperature method of graphite purification of graphite affects a number of factors: ① graphite raw material impurity content on the effect of high-temperature method of purification of the greatest impact, the impurity content of raw materials is different, the resulting products are different ash, and graphite with a high content of carbon is better ② graphite crucible carbon content is also an important factor affecting the effect of purification, the crucible ash is lower than the graphite ash, which contributes to the graphite in the ash escape; ③ the use of high-current, graphite warming fast The graphite is heated up quickly by the high current, which is favorable for graphite purification, and it is better to use the raw material of high power electrode and be processed by high temperature of 2800℃; ④ The graphite granularity also has a certain influence on the purification effect.
Graphite can be used to produce refractory materials, conductive materials, wear-resistant materials, lubricants, high-temperature-resistant sealing materials, corrosion-resistant materials, heat-insulating materials, adsorbent materials, friction materials, and radiation-resistant materials, etc., which are widely used in metallurgy, petrochemical industry, machinery industry, and electronics industry.
In the iron and steel industry, graphite refractories are used for refractory furnace linings of electric arc blast furnaces and oxygen converters, steel ladle refractory linings, etc. Graphite refractories are mainly monolithic casting materials, magnesium-carbon bricks and aluminum-graphite refractories. Graphite is also used in powder metallurgy and metal casting film-forming materials; graphite powder is added to steel to increase the carbon content of steel, so that high-carbon steel has many excellent properties.
In the electrical industry as the manufacture of electrodes, brushes, carbon rods, carbon tubes, the positive electrode of the mercury positive converter, graphite washers, telephone parts, the coating of television tubes and so on.
Graphite is often used as a lubricant in the machinery industry. Lubricants often can not be used in high-speed, high temperature, high pressure conditions, while graphite wear-resistant materials can be in the temperature of -200 ~ 2000 ℃ in a very high sliding speed, without lubricants work. Many conveying corrosive media equipment, widely used graphite materials made of piston cups, seals and bearings, they do not need to add lubricant when running. Graphite emulsion is also a good lubricant for many metal processing (wire drawing, pipe drawing).
After special processing of graphite, with corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, low permeability and other characteristics, on a large number of used in the production of heat exchangers, reaction tanks, condensers, combustion towers, absorption towers, coolers, heaters, filters, pumps equipment. Widely used in petrochemical, wet metallurgy, acid and alkali production, synthetic fiber, paper and other industrial sectors, can save a lot of metal materials.
Due to the graphite coefficient of thermal expansion is small, and can withstand rapid changes in cold and heat, can be used as a casting mold of the glassware, the use of graphite ferrous metal to get the casting size is accurate, the surface of the finished product rate is high, without processing or a little processing can be used, thus saving a lot of metal. The production of cemented carbide and other powder metallurgy processes, usually made of graphite material mold and sintering with porcelain boat. Monocrystalline silicon crystal growth crucibles, regional refining containers, bracket fixtures, induction heaters, etc. are processed from high-purity graphite. In addition, graphite can also be used as a vacuum smelting graphite insulation plate and base, high-temperature resistance furnace furnace tube and other components.
(1) Graphite can also prevent boiler scaling. Tests conducted by the relevant organizations show that adding a certain amount of graphite powder to water (about 4 to 5 grams per ton of water) can prevent scaling on the surface of the boiler. In addition, graphite can be applied to metal chimneys, roofs, bridges and pipes to prevent corrosion and rust.
Graphite deep-processed products filled with plastic products and rubber products, can make plastic products and rubber products do not produce static electricity, many industrial products need to have anti-static and shielding electromagnetic radiation function, graphite products have both functions, graphite in plastic products, rubber products and other related industrial products in the application will increase.
In addition, graphite is also the abrasive and antirust agent for glass and paper making in light industry, and it is an indispensable raw material for manufacturing pencils, ink, black lacquer, ink and artificial diamonds and diamonds. It is a good energy-saving and environmentally friendly materials, with the development of modern science and technology and industry, graphite applications are still broadening, has become an important raw material for new composite materials in high-tech fields.